
GeoVista
Our Road Asset Management project uses advanced detection to identify and geo-tag assets such as streetlights, electric poles, and OFC infrastructure. Each asset is precisely mapped with its position (left/right of the road) and accurate latitude–longitude coordinates, achieving up to 1m accuracy.
Why Needed
India’s road and urban infrastructure is expanding rapidly, yet there is limited visibility into existing roadside assets such as electric, telegraph, and lighting poles. Manual surveys are costly, time-consuming, and prone to errors. A video-based, automated system for asset extraction was needed to provide accurate, scalable, and up-to-date geospatial data for better planning, maintenance, and utility management.
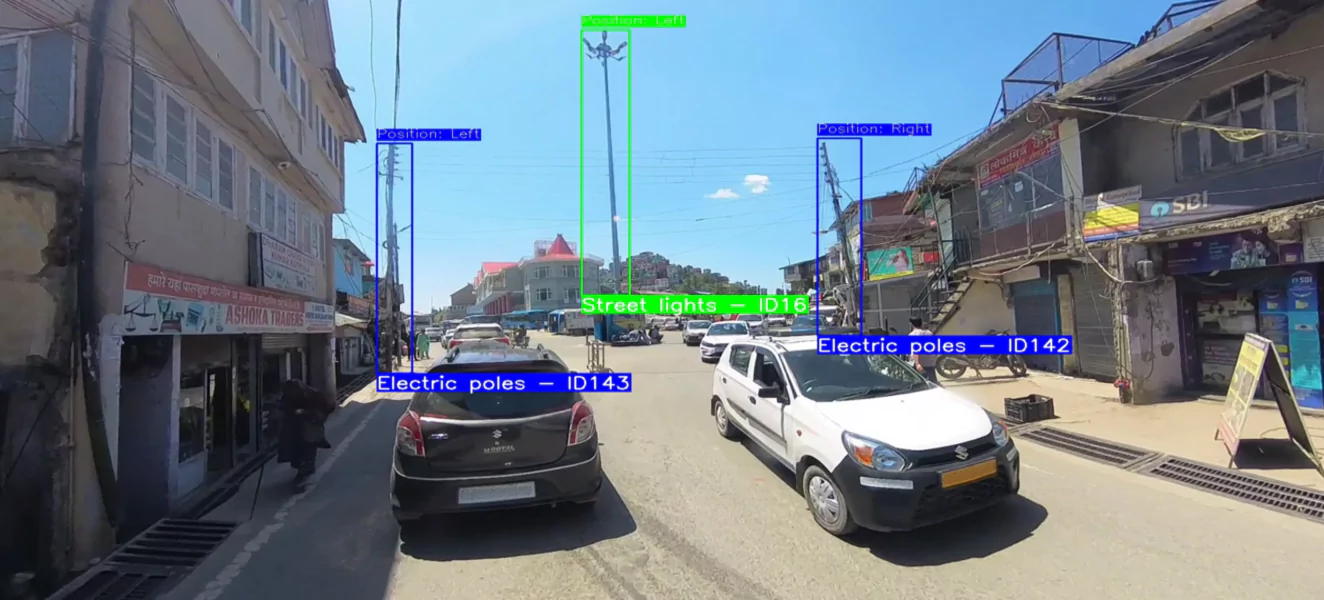
Technological Innovation
The project developed a self-hosted system capable of detecting and geolocating roadside poles directly from geotagged video. By integrating advanced AI models (detection transformers, Deep SORT) with GPS synchronization and visual odometry, the solution ensured high detection accuracy and robust geospatial positioning. To counter road undulations, sharp turns, and lens distortions, state-of-the-art video stabilization and distortion removal algorithms were applied, preserving asset geometry and improving detection and tracking performance. The WebApp further enabled interactive review, asset-layer toggling, and structured data export, delivering a complete and user-friendly workflow from raw video to validated geospatial asset inventory.
Application Sector
This technology applies across multiple domains: smart cities, road infrastructure management, utility and power companies, telecom operators, and municipal bodies. It supports infrastructure audits, planning of new networks, and ongoing maintenance of existing assets.
Socio-economic Impact
By automating pole asset extraction, the solution reduces the cost and time required for infrastructure surveys, improves accuracy of asset inventories, and helps avoid duplication or mismanagement. This translates into better planning for electricity, communication, and lighting networks, directly improving service delivery to citizens. At scale, such technology supports smart governance, enables more efficient public spending, and strengthens India’s digital infrastructure backbone.



